Allergic reactions
Allergic reactions are sensitivities to substances called allergens that come into contact with the skin, nose, eyes, respiratory tract, and gastrointestinal tract. They can be breathed into the lungs, swallowed, or injected.
Allergic reactions are common. The immune response that causes an allergic reaction is similar to the response that causes hay fever. Most reactions happen soon after contact with an allergen.
Many allergic reactions are mild, while others can be severe and life-threatening. They can be confined to a small area of the body, or they may affect the entire body. The most severe form is called anaphylaxis or anaphylactic shock. Allergic reactions occur more often in people who have a family history of allergies.
Substances that don’t bother most people (such as venom from bee stings and certain foods, medications, and pollens) can trigger allergic reactions in certain people.
First-time exposure may produce only a mild reaction. Repeated exposures may lead to more serious reactions. Once a person has had an exposure or an allergic reaction (is sensitized), even a very limited exposure to a very small amount of allergen can trigger a severe reaction.
Most severe allergic reactions occur within seconds or minutes after exposure to the allergen. Some reactions can occur after several hours, particularly if the allergen causes a reaction after it has been eaten. In very rare cases, reactions develop after 24 hours.
Anaphylaxis is a sudden and severe allergic reaction that occurs within minutes of exposure. Immediate medical attention is needed for this condition. Without treatment, anaphylaxis can get worse very quickly and lead to death within 15 minutes.
An allergic reaction is the body’s way of responding to an “invader.” When the body senses a foreign substance, called an antigen, your immune system is triggered. Immune system normally protects the body from harmful agents such as bacteria and toxins.
The overreaction to a harmless substance (an allergen) is called a hypersensitivity reaction, or common name an allergic reaction.
♦ Anything can be an allergen. Dust, plants, pollen, medications, (such as ibuprofen, sulfa drugs like trimethoprim [Bactrim] and codeine, amoxicillin [Amoxil, Amoxil Pediatric Drops, Moxatag, Trimox]), foods (common food allergies include shrimp and other shellfish, peanuts), insect bites (such as from bees or mosquitos), animal dander, viruses, or bacteria are examples of allergens.
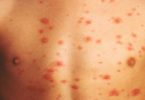
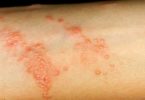
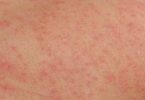
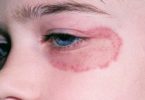
♦ Reactions can occur in one spot, such as a small localized skin rash, itchy eyes, face bumps, or all over, as in a whole body rash such as hives (urticaria).
♦ Reaction can include one or more symptoms.
Most allergic re-actions are minor, like rash from mosquito, poison ivy or other bug bites, or sneezing from hay fever. Some type of reaction depends on the person’s immune system response, that’s sometimes unpredictable.
What Are the Symptoms of an Allergic Reaction?
The symptoms of an allergic reaction can vary from mild to severe. If you are exposed to an allergen for the first time, your symptoms may be mild. These symptoms may get worse if you are repeatedly exposed to the allergen.
Symptoms of a mild allergic reaction can include:
♦ hives (itchy red spots on the skin)
♦ itching
♦ nasal congestion (rhinitis)
♦ a rash
♦ watery or itchy eyes
Severe allergic reactions can cause other symptoms such as:
♦ abdominal cramping or pain
♦ pain or tightness in the chest
♦ diarrhea
♦ difficulty swallowing
♦ dizziness (vertigo)
♦ fear or anxiety
♦ flushing of the face
♦ nausea or vomiting
♦ heart palpitations
♦ swelling of the face, eyes, or tongue
♦ weakness
♦ wheezing
♦ difficulty breathing
♦ unconsciousness
A severe and sudden allergic reaction can develop within seconds of being exposed to an allergen. This type of reaction is known as anaphylaxis and results in life-threatening symptoms, including swelling of the airway and the inability to breathe as well as a sudden dramatic drop in blood pressure. If you experience this type of allergic reaction, seek immediate emergency help. Without treatment, this condition can result in death within 15 minutes.
read more about Allergic Reaction Causes