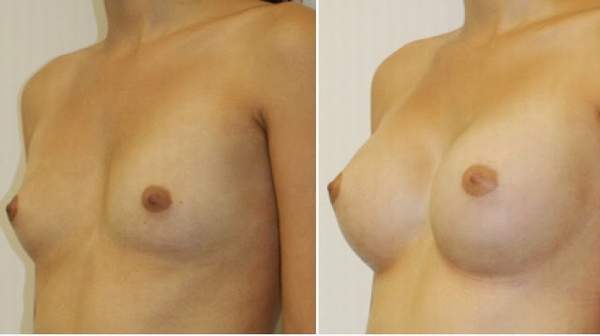
Breast augmentation surgery increases or restores breast size using silicone gel implants, saline implants or in some cases, fat transfer. One of the most popular and frequently performed aesthetic surgery procedures, breast augmentation has a long and successful track record in satisfying women who wish to enhance, regain or restore balance to their figures. Women can get breast implants to make their breasts bigger and fuller. That can be done for re-constructive purposes, such as after mastectomy for breast cancer, or for cosmetic reasons.
Deciding to have Breast Implants
The decision to have breast implants should be an informed one that takes into account the potential health risks and financial costs.
If you are considering having breast implants, it’s a good idea to speak to your GP and a cosmetic surgeon beforehand about why you want them, your expectations of surgery, the procedure itself, and the potential risks.
Take your time to find out as much as you can beforehand, and don’t feel rushed or pressured into making a decision.
The following are some common reasons why you may want to consider breast augmentation:
- You believe your breasts are too small for your body.
- You feel self-conscious wearing a swimsuit or form-fitting or low-cut tops.
- Clothes that fit your hips are too large at the bust line.
- Your breasts have become smaller or less firm after you’ve had children.
- Your breasts have become smaller due to weight loss.
- One of your breasts is noticeably smaller than the other.
Types of Breast Implants
Breast implants are artificial (prosthetic) implants. In the UK, two types of breast implants are commonly used:
- silicone gel implants available as a liquid, a gel, or a solid form similar to plastic
- saline (sterile salt water) implants
Each type has associated advantages and disadvantages, although most people choose to use implants filled with silicone.
Breast implants generally have a life expectancy of 10 to 15 years, after which they may need to be replaced.
How the Breast Implant Procedure Is Done
- Because breasts can continue to develop until a woman reaches her late teens or early 20s, the FDA requires that women be at least 18 years old to get breast augmentation with saline-filled implants and at least 22 years old to receive silicone implants.
- When picking your surgeon, look for one who has a lot of experience. You may be less likely to have complications later on if you choose a surgeon who has had at least five years of surgical training and at least two years’ experience in plastic surgery.
- Before your breast implant procedure, you will meet with your surgeon for a medical evaluation. You can talk about what you want and get feedback from the doctor. Your surgeon may ask you to stop taking certain medications a few days or weeks before your surgery.
- You can get breast augmentation done as an outpatient procedure, or you may stay overnight in the hospital.
- The procedure takes one to two hours. You will likely be given general anesthesia, during which you will be “asleep” and pain-free.
- The surgeon will make a cut under your breasts, under your arms, or around your nipples, depending on your body, the type of implant, and how much enlargement is being done.
- The surgeon will put the breast implant into a pocket above or below your chest muscle. After the implant is in place, the surgeon will close the cuts with sutures or surgical tape.
Recovery After Breast Implantation
- Your breasts will be covered with gauze after the surgery. You may have drainage tubes, which will be removed in a few days. You may need to wear a surgical bra as you heal.
- You’ll need to take it easy for a few days after your breast augmentation surgery. For instance, you shouldn’t do any heavy lifting for up to six weeks after getting your implants.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen may help relieve discomfort. Your doctor may also prescribe pain medication for you.
- You will probably have some swelling in the area where the surgery was done. Over time, the swelling should ease and the scars will fade.
If you are contemplating having breast implants, you should make sure you are aware of the potential risks.
Some of the problems that can occur as a result of having breast implants fitted include:
- infection or bleeding after surgery
- scarring
- the shrinkage of scar tissue around the implant (capsular contracture)
- the implant splitting (rupturing)
- the implant becoming creased or folded
- temporary or permanent changes to nipple sensation
- In some cases, further surgery may be needed to treat problems that develop.
- Breast implants are not designed to last a lifetime. You may need to have the implants replaced if you have complications or if the size and shape of your breasts change over time.
- Women who have silicone gel-filled implants will need to get an MRI scan three years after the implant surgery and then MRI scans about every two years to check for silent rupture. If your implants rupture, you will need to have them removed or replaced.
- Having breast implants can make it more difficult to get a mammogram, but special X-ray views can be done. There is a chance breast implants may make you more likely to get breast cancer. Breast implants also may make it harder for you to breastfeed.
What breast augmentation surgery won’t do
Breast augmentation does not correct severely drooping breasts. If you want your breasts to look fuller and to be lifted due to sagging, a breast lift may be required in conjunction with breast augmentation.
Breast lifting can often be done at the same time as your augmentation or may require a separate operation. Your plastic surgeon will assist you in making this decision.