What's in this article?
Cancer Overview
Cancer, also called malignancy, is an abnormal growth of cells. Symptoms vary depending on the type. The treatment may include chemotherapy, radiation, and surgery.

How Is Cancer Diagnosed?
The earlier is diagnosed and treated, the better the chance of its being cured. Some types of cancer such as those of the skin, breast, mouth, testicles, prostate, and rectum may be detected by routine self-exam or other screening measures before the symptoms become serious.
Prostate Cancer

Develops in a man’s prostate, the walnut-sized gland just below the bladder that produces some of the fluid in semen. It’s the most common in men after skin cancer. Prostate often grows very slowly and may not cause significant harm. But some types are more aggressive and can spread quickly without treatment.
Colorectal Cancer

is the third most frequently diagnosed in men and women and the second highest cause of deaths in the U.S. Yet, when found early, it is highly curable. This type of cancer occurs when abnormal cells grow in the lining of the large intestine (colon) or rectum.
Lung Cancer
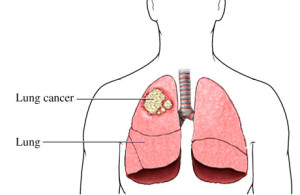
-is the top cause of deaths in both men and women. But this wasn’t always the case. Before the widespread use of mechanical cigarette rollers, lung cancer was rare.
Breast Cancer
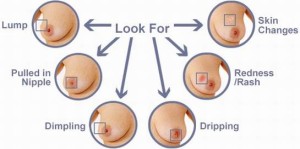
The first sign of breast cancer often is a breast lump or an abnormal mammogram. This stages range from early, curable to metastatic breast cancer.
Melanoma/Skin Cancer
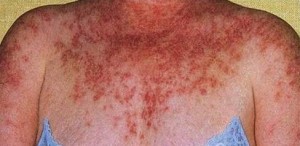
include melanoma, basal cell, and squamous cell. Basal and squamous cell are common and treatment is very effective. Malignant melanoma can be difficult to treat. Early diagnosis and treatment can increase the survival rate from melanoma.
Ovarian Cancer
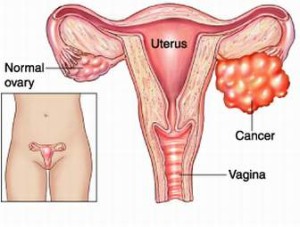
warning signs include ongoing pain or cramps in the belly or back, abnormal vaginal bleeding, nausea, and bloating. Depending on the stage, ovarian treatment includes surgery and chemotherapy.
What Are the Treatments for Cancer?

Depending on the type and stage, treatments to eradicate the tumor or slow its growth may include some combination of surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, hormone therapy or immunotherapy.





