What's in this article?
What Is a Colonoscopy?
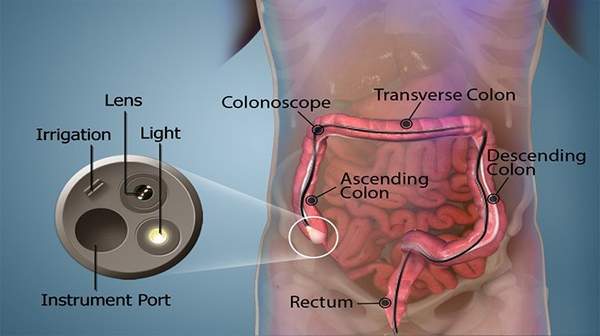
Colonoscopy is a test that allows your doctor to look at the inner lining of your large intestine (rectum and colon). He or she uses a thin, flexible tube called a colonoscope to look at the colon. A colonoscopy helps find ulcers, colon polyps, tumors, and areas of inflammation or bleeding.
Why do doctors use colonoscopy?
A colonoscopy can help a doctor find the cause of unexplained symptoms, such as
- changes in your bowel activity
- pain in your abdomen
- bleeding from your anus
- unexplained weight loss
Doctors also use colonoscopy as a screening tool for colon polyps and cancer. Screening is testing for diseases when you have no symptoms. Screening may find diseases at an early stage, when a doctor has a better chance of curing the disease.
Colonoscopy Risk
A colonoscopy poses few risks. Rarely, complications of a colonoscopy may include:
- Adverse reaction to the sedative used during the exam
- Bleeding from the site where a tissue sample (biopsy) was taken or a polyp or other abnormal tissue was removed
- A tear in the colon or rectum wall (perforation)
After discussing the risks of colonoscopy with you, your doctor will ask you to sign a consent form authorizing the procedure.
Colonoscopy procedure
Before the colonoscopy procedure, an intravenous line is inserted into the back of your hand to provide medications that make you relaxed and drowsy. You will be given medications that provide deep sedation so that you will not have any recollection of the procedure or feel pain.
Colonoscopy is performed in a unit that is used for endoscopy procedures only. The patient lies on their left-hand side with their knees tucked up to their chest. The colonoscope is gently inserted through the anus and up into the colon, and air or carbon dioxide is introduced to help the colonoscope pass.
Once the colonoscope has reached the point where the colon joins the small intestine, the doctor slowly withdraws it while looking carefully at the colon lining. Photographs may be taken. The procedure generally takes 15 to 30 minutes..
If colon polyps are found during a colonoscopy, they are removed and the tissue is sent for analysis to determine if the polyp is cancerous. Polyp removal or biopsy may cause bleeding. Bleeding may be stopped during the procedure using clips or other methods. If the bleeding is severe, it may require blood transfusion or re-insertion of the colonoscope to control the bleeding.
Colonoscopy preparation
If the procedure is to be complete and accurate, the colon must be completely cleaned, and there are several colonoscopy preparations. Patients are given detailed instructions about the cleansing preparation. In general, this consists of drinking a large volume of a special cleansing solution or several days of a clear liquid diet and laxatives or enemas prior to the examination. These instructions should be followed exactly as prescribed or the procedure may be unsatisfactory (visualization of the lining of the colon may be obscured by residual stool), and it may have to be repeated, or a less accurate alternative test may be performed in its place.
What should I expect after a colonoscopy?
After a colonoscopy, you can expect the following:
- You’ll stay at the hospital or outpatient center for 1 to 2 hours after the procedure.
- You may have abdominal cramping or bloating during the first hour after the procedure.
- The sedatives or anesthesia takes time to wear off completely.
- You should expect a full recovery by the next day, and you should be able to go back to your normal diet.
- After the procedure, you—or a friend or family member—will receive instructions on how to care for yourself after the procedure. You should follow all instructions.
- A friend or family member will need to drive you home after the procedure.
If the doctor removed polyps or performed a biopsy, you may have light bleeding from your anus. This bleeding is normal. Some results from a colonoscopy are available right after the procedure. After the sedatives or anesthesia has worn off, the doctor will share results with you or, if you choose, with your friend or family member. A pathologist will examine the biopsy tissue. Biopsy results take a few days or longer to come back.
Colonoscopy side effects
Colonoscopy is a safe procedure, although complications may rarely occur. These include:
- excessive bleeding
- perforation or puncture of the colon wall.