What's in this article?
Cutaneous Candidiasis Overview
Cutaneous candidiasis and other forms of candidosis are infections caused by the yeast Candida albicans or other Candida species. Yeasts are unicellular fungi that typically reproduce by budding, a process that entails a progeny pinching off of the mother cell. C albicans, the principal infectious agent in human infection, is an oval yeast 2-6 µm in diameter. C albicans (as well as most medically significant fungi) has the ability to exist in both hyphal and yeast forms (termed dimorphism). If pinched cells do not separate, a chain of cells is produced and is termed pseudohyphae.
Superficial infections of skin and mucous membranes are the most common types of candidal infections of the skin. Common types of candidal skin infection include intertrigo, diaper dermatitis, erosio interdigitalis blastomycetica, perianal dermatitis, and candidal balanitis. In certain subpopulations, candidal infection of the skin has increased in prevalence in recent years, principally because of the increased numbers of patients who are immunocompromised.
Esophagitis, septicemia, endocarditis, peritonitis, and urinary tract infections are less frequent types of candidosis. Although C albicans is the most common cause of human infection, the genus Candida includes more than 150 species. Candida tropicalis, Candida parapsilosis, Candida guilliermondi, Candida krusei, Candida kefyr, Candida zeylanoides, and Candida glabrata (formerly Torulopsis glabrata) are less common causes of human disease.
Causes of Cutaneous Candidiasis infection of the skin
The body normally hosts a variety of germs, including bacteria and fungi. Some of these are useful to the body, some produce no harm or benefit, and some can cause harmful infections.
Some fungal infections are caused by fungi that live on the hair, nails, and outer skin layers. They include yeast-like fungi such as Candida.
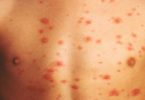
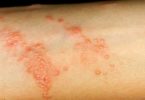
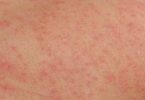
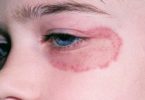
In cutaneous candidiasis, the skin is infected with Candida fungi. This type of infection is fairly common. It can involve almost any skin on the body, but most often it occurs in warm, moist, creased areas such as the armpits and groin. The fungus that most often causes cutaneous candidiasis is Candida albicans.
Candida is the most common cause of diaper rash in infants. The fungi take advantage of the warm, moist conditions inside the diaper. Candida infection is particularly common in people with diabetes and in those who are obese. Antibiotics, steroid therapy, and chemotherapy increase the risk of cutaneous candidiasis. Candida can also cause infections of the nails, edges of the nails, and corners of the mouth.
Oral thrush, a form of Candida infection of the moist lining of the mouth, usually occurs when people take antibiotics. It may also be a sign of an HIV infection or other weakened immune system disorders when it occurs in adults. Individuals with Candida infections are not usually contagious, though in some settings people with weakened immune systems may catch the infection.
Candida is also the most frequent cause of vaginal yeast infections. These infections are common and often occur with antibiotic use.
People with seriously weakened immune systems and cutaneous candidiasis may go on to develop more serious Candida infections inside their body.
Exams and Tests of Cutaneous Candidiasis
Your doctor or nurse can usually diagnose this condition by looking at your skin. The health care provider may gently scrape off a sample of skin for testing.
Older children and adults with a yeast skin infection should be tested for diabetes. High sugar levels seen in people with diabetes act as food for the yeast fungus, and help it grow.
Possible Complications of Cutaneous Candidiasis
These complications may occur:
- Infection of the nails may cause the nails to become oddly shaped and may cause an infection around the nail.
- Candida skin infections may return.
- Widespread candidiasis may occur in people with weakened immune systems.