What's in this article?
What is Cutaneous candidiasis?
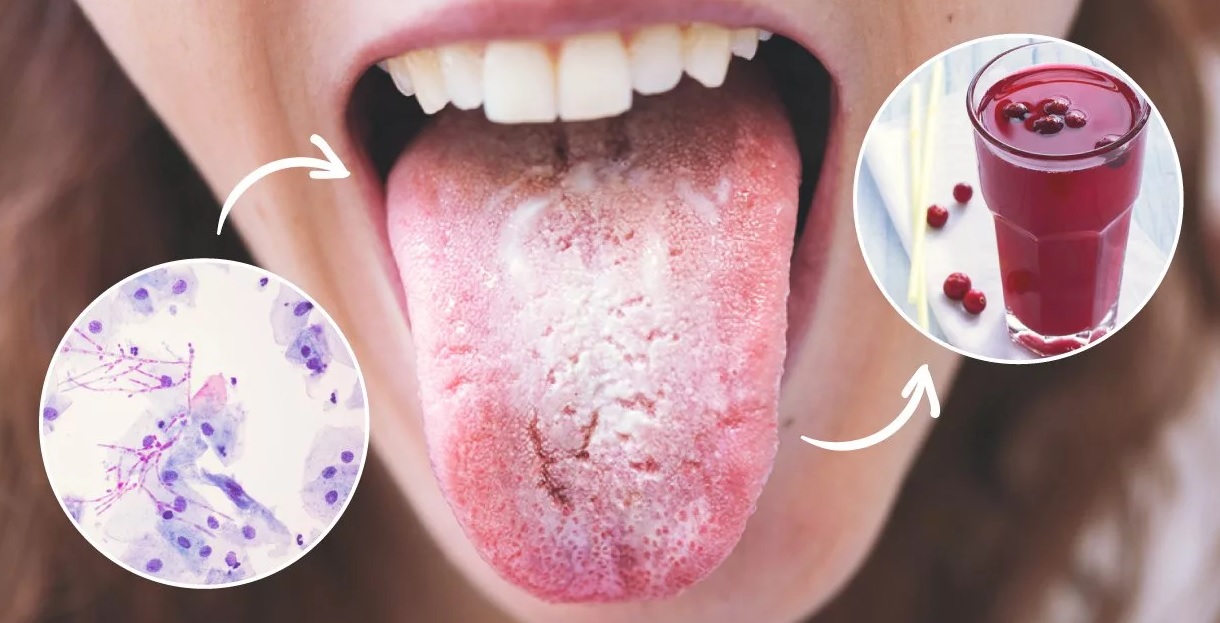
Cutaneous candidiasis is a type of fungus that can cause an infection in your skin. In normal conditions, your skin may host small amounts of this fungus, but problems arise when it begins to multiply and creates an overgrowth. More than 150 species of candida exist, but the majority of infections are caused by a species called candida albicans.
Cutaneous candidiasis skin infections can occur on almost any area of the body, but are more commonly found in intertriginous regions where two skin areas may touch or rub together such as armpits, the groin, skin folds, and the area between the fingers and toes. The fungus thrives in warm, moist, and sweaty conditions.
Normally, your skin acts as an effective barrier against infection, but any cuts or breakdown in the superficial layers of the skin may allow the fungus to cause infection.
The prognosis for candidal infections is often very good. Generally, the condition isn’t serious and can be easily treated.
Causes of Candidiasis
The body normally hosts a variety of germs, including bacteria and fungi. Some of these are useful to the body, some produce no harm or benefit, and some can cause symptoms or, at times, harm.
The fungus that most often causes candida skin infections is Candida albicans. These fungi take advantage of the warm, moist conditions. Skin infections caused by Candida may be found:
♦ In the diaper area in babies
♦ In the armpits, groin, and underneath the breasts
♦ At the corners of the mouth (angular cheilitis)
♦ In toenails, or at the edge of the nails (paronychia)
Candida infection is more common in people with:
♦ A weakened immune system due to certain medicines and diseases, such as AIDS
♦ Diabetes
♦ Obesity
You are more likely to get a candida infection if you take high doses of antibiotics or taken them for a long time. Antibiotics kill some of the healthy bacteria that help keep the fungus from over growing.
Candida also causes vaginal yeast infections and thrush, which affects the mouth.
Symptoms of Candidiasis
A yeast (candida) infection of the skin can cause intense itching.
Symptoms also include:
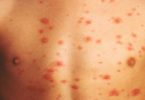
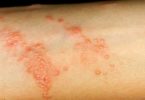
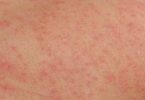
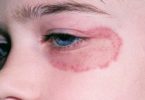
♦ Red, growing skin rash
♦ Rash on the skin folds, genitals, middle of the body, buttocks, under the breasts, and other areas of skin
Recognizing the Symptoms of Candidiasis of the Skin
Candidiasis of the skin can occur anywhere on the skin, but it is most likely to occur on areas where the skin is folded. This includes areas in the armpits, in the groin, between your fingers, and under your breasts.
Rashes from candidiasis can appear either as white or red skin. Candidiasis between the fingers can appear moist, white in color, and peeling, and can be painful and irritating. The infection also may appear red and rash-like, which can cause you to feel itchy and hot. The skin infection can progress to cause cracking and soreness. Blisters and pustules can also occur.
Exams and Tests of Candidiasis
Your doctor or nurse can usually diagnose this condition by looking at your skin. The health care provider may gently scrape off a sample of skin for testing.
Older children and adults with a yeast skin infection should be tested for diabetes. High sugar levels seen in people with diabetes act as food for the yeast fungus, and help it grow.
How is Candidiasis Treated?
Proper hygiene is vital to keeping candida infections at bay. This includes washing the skin regularly and thoroughly drying it to prevent moisture.
Because poor blood sugar control can contribute to candida infections, maintaining optimal blood sugar levels can help. This may include reducing the amount of sugar in your diet, and, if you are diabetic, being careful to follow your doctor’s instructions to control your blood sugar.
Your physician may recommend using an antifungal cream or powder applied to your skin to reduce candida’s spread. In most instances, you will not need to take an oral antifungal medication to kill the yeast. However, if your candida infection is located inside your body, such as your throat, mouth, or vagina, you may need to take oral medication.