What's in this article?
What is discoid eczema?
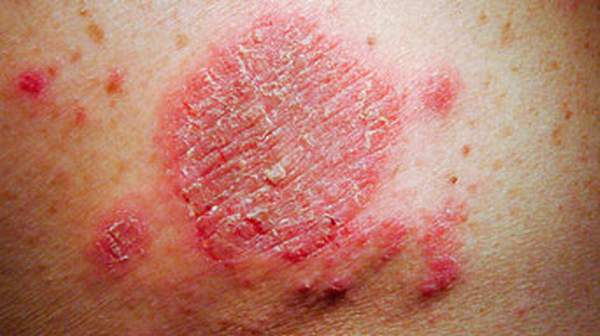
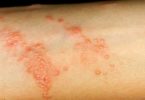
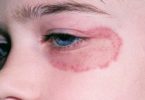
Discoid eczema is a common type of eczema/¬dermatitis, in which there are scattered roundish patches of eczema. They can be intensely itchy. The rash is also called nummular dermatitis.
Discoid eczema, also known as discoid dermatitis, gravitational eczema,nummular dermatitis, and nummular eczema is a form of dermatitis. It is a chronic (long-term) or recurrent condition. A rash appears on the skin in the form of red coin shaped discs – plaques of eczema – which can affect different parts of the body, but primarily the lower legs, hands and forearms, and sometimes the trunk. It is extremely itchy and uncomfortable. Dermatitis means “inflammation of the skin”.
What is the cause of discoid eczema?
The cause of discoid eczema is unknown. Some cases are associated with Staphylococcus aureus infection.
The eruption can be precipitated by:
- Localised injury such as scratch, insect bite or thermal burn
- Impetigo or wound infection
- Contact dermatitis
- Dry skin
- Varicose veins (varicose eczema)
- Another skin problem
How common is discoid eczema and who gets it?
Discoid eczema is quite common and probably affects about 2 in 1,000 people. It seems to be more common in men than in women. Discoid eczema can affect men and women of any age but it most commonly affects people aged between 50 and 65. It also affects women between the ages of 15 and 25. It is rare in children.
What are the signs and symptoms of discord eczema?
A symptom is something the patient senses and describes, while a sign is something other people, such as the doctor notice. For example, drowsiness may be a symptom while dilated pupils may be a sign.
- The affected areas are red and have well-defined edges.
- On top of the coin-shaped plaques there may be small blisters, scales or yellowish crusts – often a sign of a staphylococcal (bacterial) infection.
- Typically, the affected areas are symmetrical, especially on the limbs.
- The lesions (affected areas) are extremely itchy, often resulting in lichenification (see next line).
- Lichenification – constant scratching and rubbing leads to thick, leathery skin. Prolonged scratching and rubbing causes the epidermis (outer layer of skin) to become overgrown (hypertrophied). The skin thickens and there are exaggerated skin markings; giving the skin an appearance like leathery bark.
- Apart from itching, affected areas may also burn or sting.
- Itching tends to be worse at night.
- Symptoms most commonly appear on the legs, but may also do so on the arms, trunk, hands or feet. The face and scalp are not affected.
How discoid eczema is treated
Discoid eczema is usually a long-term problem, but medications are available to help relieve the symptoms and keep the condition under control.
Treatments used include:
- emollients – moisturisers applied to the skin to stop it becoming dry
- topical corticosteroids – ointments and creams applied to the skin that can help relieve severe symptoms
- antihistamines – medications that can reduce itching and help you sleep better
There are also things you can do yourself to help, such as avoiding all the irritating chemicals in soaps, detergents, bubble baths and shower gels.
Additional medication can be prescribed if your eczema is infected or particularly severe.