What's in this article?
What is Eczema?
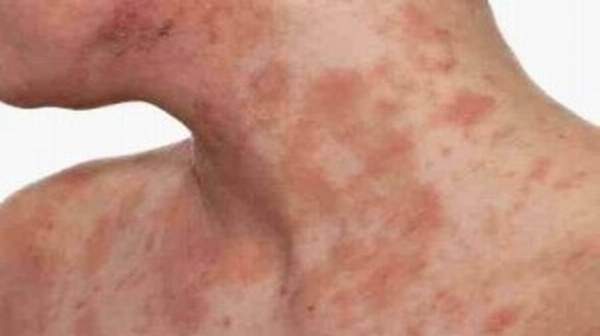
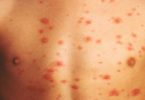
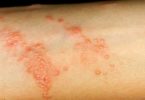
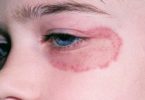
Eczema symptoms include itchy, red, and dry skin caused by inflammation. It’s most commonly found in children, although adults can get it. It is also called atopic dermatitis and is treated with oral medications, steroid creams and light therapy .
The term “eczema” refers to a set of clinical characteristics. Classification of the underlying diseases has been haphazard and unsystematic, with many synonyms used to describe the same condition. A type of eczema may be described by location by specific appearance or by possible cause.
Eczema is a term for a group of medical conditions that cause the skin to become inflamed or irritated. The most common type is known as atopic dermatitis, or atopic eczema. Atopic refers to a group of diseases with an often inherited tendency to develop other allergic conditions, such as asthma and hay fever.
What Are the Types of Eczema?
When people refer to eczema, they usually mean atopic dermatitis, which is the common and chronic type. Other types include:
- Contact dermatitis is caused by contact with irritants. Burning, itching, and redness occur. When the irritant is removed, the inflammation goes away.
- Dyshidrotic dermatitis affects fingers, palms of the hand, and soles of the feet. It causes itchy, scaly patches of skin that flake constantly or become red, cracked, and painful. The condition is more common in women.
- Nummular dermatitis causes dry, round patches of skin in the winter months. It usually affects the leg. It is more common in men.
- Seborrheic dermatitis causes itchy, red, scaly rashes, particularly on the scalp, on the eyebrows, on the eyelids, on the sides of the nose, and behind the ears.
What Causes Eczema?
The exact cause of eczema is unknown, but it’s thought to be linked to an overactive response by the body’s immune system to an irritant. It is this response that causes the symptoms.
In addition, eczema is commonly found in families with a history of other allergies or asthma. Also, defects in the skin barrier could allow moisture out and germs in.
How Is Eczema Diagnosed?
A pediatrician, dermatologist, or your primary care provider can make a diagnosis of eczema. While there are no tests to determine eczema, most often your doctor can tell if it’s eczema by looking at your skin and by asking a few questions.
Since many people with eczema also have allergies, your doctor may perform allergy tests to determine possible irritants or triggers. Children with eczema are especially likely to be tested for allergies.
What Are the Risk Factors of Eczema?
Several factors can increase the risk of developing eczema.
Eczema is more common in children who suffer from asthma and/or hay fever or who develop these conditions later, usually before the age of 30.
People with family members who have eczema are also at higher risk of developing the disease.