What's in this article?
What is Hand Fungus?
Different fungus affects different parts of the body. Hand fungus is caused by the genus dermatophytes. These dermatophytes affect the skin and are commonly referred to as ringworm.
Fungi are a type of microorganisms that have a wide range of types and occurrences. Till date, about 100,000 different species of fungi have been identified. While fungi are used extensively in the food and drug industry, they also cause many serious diseases in human beings. Some of the different fungal infections in human beings are listed below.
- Aspergillosis (a bronchopulmonary allergic reaction caused by the fungus aspergillus)
- Candidoses (thrush caused by the yeast candida albicans)
- Coccidioidomycosis (valley fever or desert rheumatism caused by the fungus coccidioides)
- Cryptococcosis (fatal fungal infection seen in immunodeficient conditions such as AIDS)
- Histoplasmosis (a fungal lung disease, also known as Darling’s disease or cave disease)
- Eumycetoma (fungal infection that affects the foot, also known as Madura foot)
- Paracoccidioidomycosis (fungal systemic infection that affects the lymph nodes and the mucous membranes, lungs and bones)
- Dermatophytosis or ringworm (fungal infection of the skin)
In this article, we will discuss hand fungus, the causes for fungus on hands, and what your home remedy options are.
How to Deal With Hand Fungus
Hand fungus can be dealt with home remedies or different medications. Treatments are usually designed for clearing the infection. However, in certain cases, this condition tends to recur. Home remedies help you save money and are quite helpful as well. However, if they fail, you need to resort to proper medications according to the type of your hand fungus.
Causes of Hand Fungus
There are many different dermatophytes, and each of them affects a particular part of the body. However, there are only three types of hand fungal infections. Let’s take a look at these in detail.
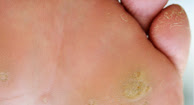
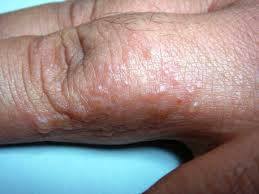
Fungus of the hands (tinea manuum): Tinea mannum is the fungus that affects the hands and the palms. Commonly, it is seen on the fingers. Some of the symptoms of this kind of infection are as follows.
- Scaly or crackling skin
- Itching and burning of the infected area
- Inflammation
Types of Fungal Skin Infections
Fungal skin infections are divided into groups, depending on what type of organism is involved. The full name depends on where the infection is found on your body. Some common fungal skin infections are listed below.
Dermatophyte infections
Most basic fungal skin infections are caused by dermatophytes — types of fungi that cause skin, nail and hair infections. They are very common. Dermatophyte infections include the following:
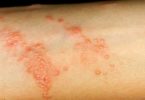
- Athlete’s foot (tinea pedis and tinea manuum). Around one in four adults have athlete’s foot (tinea pedis) at some time in their lives. It can be caused by a combination of fungi and bacteria, which makes your skin itchy, dry, scaly and red. Sometimes it causes blisters and cracked skin. It’s especially common between your toes. You often pick up athlete’s foot from coming into contact with contaminated skin left behind in swimming pools, showers and saunas. If you don’t wash your hands after touching a contaminated area, it can spread to your hands where it’s known as tinea manuum. This mostly affects the creases on your palms and sides of your fingers.
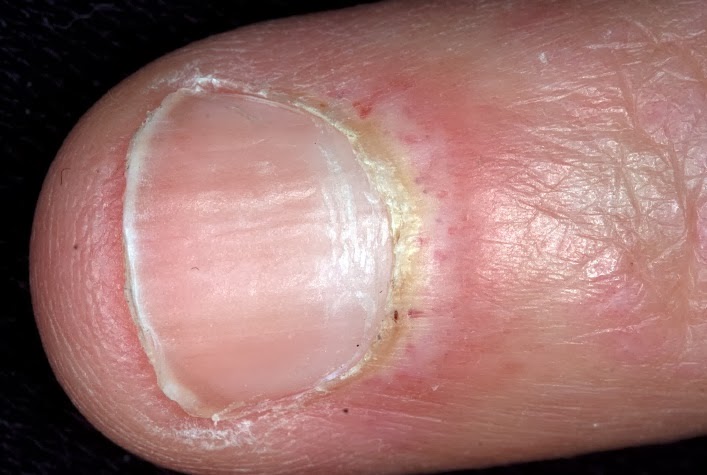
- Nail infections. Onychomycosis is the name for any fungal nail infection. Tinea unguium (ringworm of your nails) is a common infection. Your nails become malformed, thickened and crumbly. Not all nails affected like this are caused by fungal infections, but it’s a common cause. Toenail infections are commonly linked with athlete’s foot. Your fingernails can be affected too.
- Ringworm of the groin (tinea cruris). This is often called ‘jock itch’ because it occurs in sportspeople and is common among young men. It causes an itchy, red rash in your groin and the surrounding area and is usually seen in men who’ve been sweating a lot. Often you’ll also have athlete’s foot, as the infection can be spread by scratching your groin after scratching your infected feet.
- Ringworm on the body (tinea corporis). This often affects exposed areas of your body, such as your abdomen (tummy) or your limbs, causing red raised or flat patches and rings that can merge, grow and spread from the centre. The rings are scaly at the edge surrounding clear skin in the middle.
- Ringworm of the scalp (tinea capitis). This usually affects young children. It can cause hair loss and inflammation of the affected area. You can be infected by this fungus without developing any symptoms, and become a carrier instead, spreading the infection to others, sometimes for years.
Yeast infections
Yeast infections include the following:
- Thrush. The fungus Candida albicans usually lives naturally in us and rarely causes problems. However, in certain situations, such as if you’re ill, have poorly controlled diabetes, are pregnant or using antibiotics, the fungi multiply and can cause thrush symptoms.
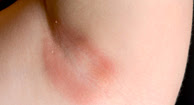
Thrush can affect your mouth and tongue, areas lined with a mucus membrane such as your vagina, and other moist, folded skin. Thrush infection often looks like small white patches, which leave a red mark when rubbed off. In adults, vaginal thrush can cause itchiness and a thick, white discharge. Thrush sometimes affects men, causing a painful red rash on the head of the penis (glans). It also commonly affects newborn babies in the mouth (oral thrush) where the white patches may be mistaken for breast or formula milk. It isn’t usually serious, but babies with thrush in their throats may stop feeding properly. Babies may also develop thrush in the nappy area. - Intertrigo. This is also caused by the normally harmless fungus Candida albicans, which lives on your skin and in your digestive system. It affects areas where skin touches skin and the environment is warm and moist, such as your armpits, groin, and under heavy breasts or fat folds. It can cause itching, soreness, spots and scales, creating a white-yellow curd over the infected area.
- Pityriasis versicolor. This infection causes dark patches to form on pale or untanned skin and light patches on tanned or darker skin. Another name for this condition is tinea versicolor (versicolor means ‘of various colours’).
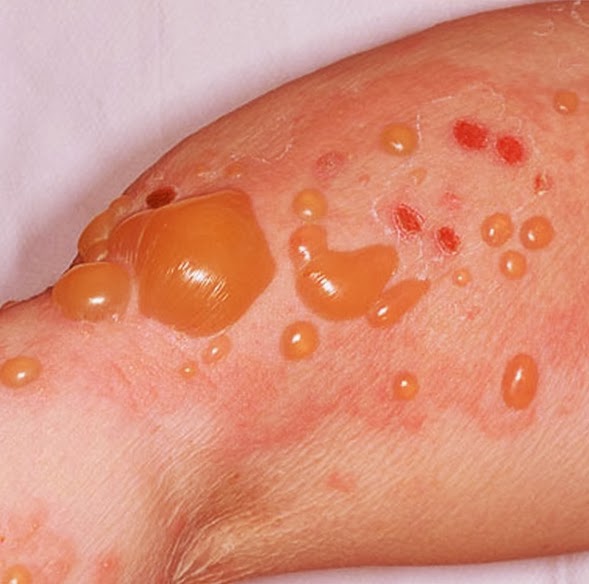
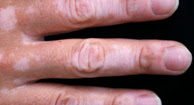
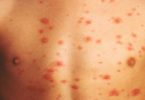
Pictures of Hand Fungus and Other Skin Problems
Dyshidrotic Eczema
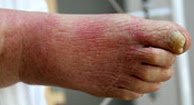
Erysipelas
Actinic Keratosis

Ingrown Nails
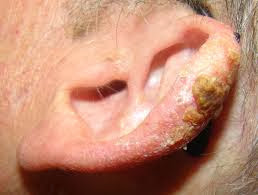
Necrotizing Fasciitis
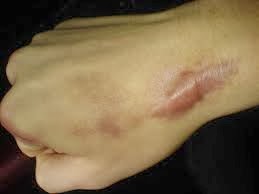
Pemphigoid
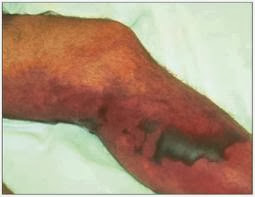
Stasis Dermatitis and Leg Ulcers
Vitiligo
To see more about Skin Condition