What's in this article?
 Heat rash (prickly heat) – Overview
Heat rash (prickly heat) – Overview
Heat rash also called prickly heat or miliaria- is a red or pink rash usually found on body areas covered by clothing. It can develop when the sweat ducts become blocked and swell and often leads to discomfort and itching. Heat rash is most common in babies, but it may affect adults in hot, humid climates.
Heat rash develops when your sweat glands commonly referred to as pores become blocked and perspiration is trapped under your skin. Symptoms range from superficial blisters to deep, red lumps. Some forms of heat rash can be intensely itchy or cause a prickly feeling.
Sweat glands are located in the dermis or deep layer of the skin, and are regulated by the temperature control centers in the brain. Sweat from the gland gets to the surface of the skin by a duct.
Facts about Heat rash
- Heat rash occurs when the skin’s sweat glands are blocked and the sweat produced cannot get to the surface of the skin to evaporate. This causes inflammation that results in a rash.
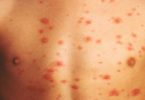
- Common symptoms of heat rash include red bumps on the skin, and a prickly or itchy feeling to the skin (also known as prickly heat).
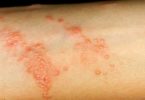
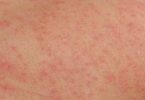
- The rash appears as reddened skin with tiny blisters and is due to inflammation. It often occurs in skin creases or areas of tight clothing where air cannot circulate.
- Heat rash usually fades when the skin is allowed to cool. Medical treatment is necessary only if the area becomes infected.
- Heat rash can be prevented by avoiding hot, humid conditions, wearing lose fitting clothes and using air conditioning or fans to allow air to circulate.
read more about difference between heat rash and hiv rash
Symptoms of Heat rash
The common symptoms of heat rash are red bumps on the skin, and an itchy or prickly feeling to the skin. These are due to inflammation of the superficial layers of the skin (the epidermis) and the prickly sensation is similar to the feeling of mild sunburn.
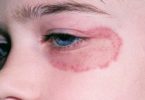
Heat rash looks like dots or tiny pimples. In young children, heat rash can appear on the head, neck, and shoulders. The rash areas can get irritated by clothing or scratching, and, in rare cases, a secondary skin infection may develop.
read more about Symptoms of Heat Rash
Three types of miliaria
Miliaria crystallina
The mildest form of heat rash affects the sweat ducts in the topmost layer of skin. Miliaria crystallina is marked by:
- Clear, fluid-filled blisters and bumps (papules) that break easily
The blisters that occur with miliaria crystallina aren’t itchy or painful. This type of heat rash usually clears on its own but can come back if hot, humid weather persists. And though it’s common in newborns, adults can develop it, too.
Miliaria profunda
A less common form of heat rash, miliaria profunda occurs mainly in adults who have had repeat bouts of miliaria rubra. It affects the dermis, a deeper layer of skin, and appears soon after exercise or any activity that causes sweating. Signs and symptoms may include:
- Firm, flesh-colored lesions that resemble goose bumps
- A lack of perspiration, which may lead to symptoms of heat exhaustion, such as dizziness, nausea and a rapid pulse
Miliaria rubra
Occurring deeper in the outer layer of skin (epidermis), miliaria rubra is sometimes called prickly heat. Adults usually develop miliaria rubra after they’re exposed to hot, humid weather or if they’re confined to bed rest. Infants usually develop this type of heat rash between the first and third weeks of life. Signs and symptoms typically include:
- Red bumps
- Itchy or prickly feeling in the affected area
- Little or no sweating in the affected areas (anhidrosis)
Occasionally, miliaria rubra vesicles become pustular and then are called miliaria pustulosa.
read more about Heat Rash Pictures, Causes and Treatments
Treatment for heat rash?
Most prickly heat rash heal on their own. The following steps can help relieve symptoms.
- Start by removing or loosening your baby’s clothing and move him or her to a cool, shady spot.
- Let the skin air-dry instead of using towels.
- If your baby’s skin is irritable when touched, calamine lotion or hydrocortisone cream may be used with your doctor’s approval.
- Avoid ointments or other lotions because they can irritate the skin.