What's in this article?
What is Scabies?
Scabies is a very itchy rash caused by a parasitic mite that burrows in the skin surface. The human scabies mite’s scientific name is Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis.
Scabies causes
The human itch mite causes scabies. People get scabies when the mite burrows into the skin. You can get the mite on your skin through:
- Direct skin-to-skin contact.
- Contact with an infested object such as a towel, bedding, or upholstered furniture.
You cannot get scabies from an animal that has mites. Only humans get this type of scabies.
Most people will not get scabies from a handshake or hug. The skin-to-skin contact must be longer for a mite to crawl from one person to another. Adults often get scabies through sexual contact.
Scabies symptoms
After the initial exposure to scabies, it can take up to six weeks for symptoms to appear. The symptoms usually develop more quickly in people who’ve had scabies before.
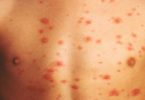
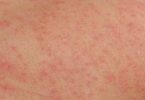
The hallmark symptoms of scabies include a rash and intense itching that gets worse at night. Continuous scratching of the infected area can create sores that become infected. If this occurs, additional treatment with antibiotics for the skin infection may be indicated.
In babies and toddlers, the most commonly infected areas are the:
- head
- face
- neck
- hands
- soles of the feet
Common sites for the rash in older children and adults include the:
- wrist
- elbow
- armpit
- nipple
- penis
- waist
- buttocks
- area between the fingers
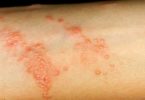
The rash itself can consist of tiny blisters or pimple-like bumps. The burrow tracks of the mite can also be seen on the skin. They may appear as tiny raised or discolored lines.
Some people with scabies may develop another form of scabies known as Norwegian scabies or crusted scabies. This is a more severe and extremely contagious type of scabies. People with crusted scabies develop thick crusts of skin that contain thousands of mites and eggs.
Crusted scabies doesn’t always cause an itchy rash. Instead, it can lead to other symptoms, such as widespread crusts on the skin that are:
- thick
- gray
- crumble easily when touched
Crusted scabies usually develops in people with weakened immune systems. This includes people with HIV or AIDS, people who use steroids or other treatments such as certain medications for rheumatoid arthritis, or people who are undergoing chemotherapy. The scabies mites can overpower the immune system more easily and multiply at a quicker rate. It’s spread in the same way as normal scabies.
Scabies contagious
Scabies is contagious. However, it usually requires fairly long skin-to-skin contact with an infested person (for example, carrying a person, sleeping with the person, or sexual partners). Infrequently, it may be contagious through contact with clothing or bedding, but this form of transfer of scabies is thought to be very infrequent. In general, most people who become infested with scabies usually have about 10-15 itch mites on their body. One exception to this rule is a scabies infestation that is seen less frequently called crusted or Norwegian scabies, in which large areas of skin are infected with huge numbers (thousands) of itch mites; a person with this type of scabies is highly contagious.
Although pets can become infested with similar itch mites, they are not usually spread from humans to animals or from animals to humans.
Scabies mite
Scabies mites are called Sarcoptes scabiei. They feed using their mouths and front legs to burrow into the outer layer of skin (epidermis), where they lay eggs.
After three to four days, the baby mites (larvae) hatch and move to the surface of the skin, where they mature into adults.
Scabies like warm places, such as skin folds, between the fingers, under fingernails, or around the buttock or breast creases. They can also hide under watch straps, bracelets or rings.
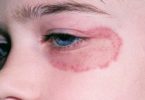
Crusted scabies
Crusted (Norwegian) scabies is a rare, severe form of scabies. It is extremely contagious because of the large number of mites found in and on the skin.
This form of scabies may occur in:
- People who have certain nutritional disorders, infectious diseases, leukemia, or weakened immune systems (such as people who have AIDS). Testing for HIV infection may be appropriate for people who have this type of scabies.
- People who have mental or nervous system disorders that mask the itching sensation. When scabies itching goes undetected, the infestation can become severe.
Characteristics of this form of scabies include:
- Scaly, crusted sores on the hands, feet, scalp, face, torso, and pressure-bearing areas such as the elbows. Facial skin may flake off, and significant hair loss can result.
- Mild itching despite the heavy infestation of mites.
- Slow response to treatment compared with other forms of scabies. When multiple treatments are ineffective, oral treatment with the medicine ivermectin may be used.
How long does the Scabies mite live?
The life cycle of the scabies mite starts when the female tunnels (burrows) into the skin and deposits her eggs. Larvae hatch from the eggs within three to 10 days and molt to become nymphs. Nymphs mature into adults that deposit additional eggs and live approximately four weeks. Burrowing and movement of the mites cause intense itching due to a type of allergic reaction to mite proteins. If the person has never been exposed to scabies before, he or she may not show symptoms until four to six weeks after the initial infestation. Individuals who have been exposed in the past usually show symptoms within a few days.
Scabies images




Scabies home remedy
Curing scabies is rather easy with the administration of prescription scabicide drugs. There are no approved over-the-counter preparations that have been proved to be effective in eliminating scabies, and home remedies are not effective. The following steps should be included in the treatment of scabies:
- Apply a mite-killer like permethrin (Elimite). These creams are applied from the neck down, left on overnight, then washed off. This application is usually repeated in seven days. Permethrin is approved for use in people 2 months of age and older and is considered to be the safest and most effective treatment for scabies.
- An alternative treatment is 1 ounce of a 1% lotion or 30 grams of cream of lindane, applied from the neck down and washed off after approximately eight hours. Since lindane can cause seizures when it is absorbed through the skin, it should not be used if skin is significantly irritated or wet, such as with extensive skin disease, rash, or after a bath. As an additional precaution, lindane should not be used in pregnant or nursing women, the elderly, people with skin sores at the site of the application, children younger than 2 years of age, or people who weigh less than 110 pounds. Lindane is not a first-line treatment and is only recommended if patients cannot tolerate other therapies or if other therapies have not been effective. Resistance to this medication has also been frequently reported.


Leave a Comment