What's in this article?
Insect Bites and Stings Definition
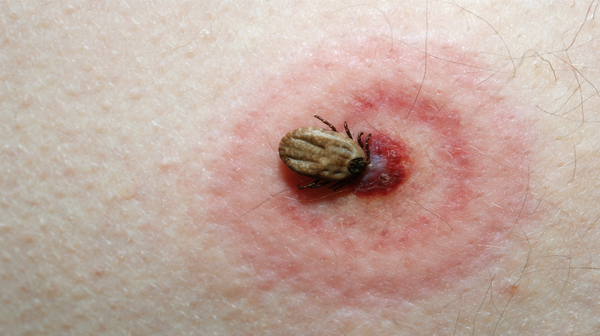
Stings and bites from insects are common. They often result in redness and swelling in the injured area. Sometimes a sting or bite can cause a life-threatening allergic reaction or transmit pathogens (viruses, bacteria or parasites, for example) to humans.
Arthropods are insects that live primarily on land and have six legs. They dominate the present-day land fauna. They represent about three-fourths of known animal life. In fact, the actual number of living species is not known and is estimated to be over 10 million.
The orders that contain the greatest numbers of species are:
- Coleoptera (beetles),
- Lepidoptera (butterflies and moths),
- Hymenoptera (ants, bees, wasps), and
- Diptera (true flies).
However, the majority of people lump insects, arthropods, and anything small that bites or stings as a “bug” or an insect. The goal of this article is to provide an overview of biting and stinging insects or bugs without making strict scientific definitions of insects or bugs. The article covers the predominant biting and stinging bugs seen or imported to the US recently, but does not cover every possible stinging or biting bug or insect worldwide
Bug bites and stings usually are just annoying, causing temporary discomfort and pain, but no serious or lasting health problems. But sometimes, they can cause infections that require treatment and allergic reactions that can be serious, even fatal.
Insect bites and stings can cause an immediate skin reaction. The bite from fire ants and the sting from bees, wasps, and hornets are usually painful.
Insect bites and stings are common and usually only cause minor irritation. However, some stings can be painful and trigger a serious allergic reaction.
Symptoms of an Insect Bite or Sting
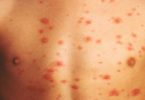
When an insect bites, it releases saliva that can cause the skin around the bite to become red, swollen and itchy.
The venom from a sting often also causes a swollen, itchy, red mark (a weal) to form on the skin. This can be painful, but it’s harmless in most cases. The affected area will usually remain painful and itchy for a few days.
The severity of bites and stings varies depending on the type of insect involved and the sensitivity of the person.
In rare cases, some people can have a serious allergic reaction(anaphylaxis) to a bite or sting that requires immediate medical treatment.
The non-emergency symptoms vary according to the type of insect and the individual. Most people have localized pain, redness, swelling, or itching. You may also feel burning, numbness, or tingling.
Prevention for Insect Bite or Sting
- Avoid provoking insects whenever possible.
- Avoid rapid, jerky movements around insect hives or nests.
- Avoid perfumes and floral-patterned or dark clothing.
- Use appropriate insect repellants and protective clothing.
- Use caution when eating outdoors, especially with sweetened beverages or in areas around garbage cans, which often attract bees.
- For those who have a serious allergy to insect bites or stings, carry an emergency epinephrine kit (which requires a prescription). Friends and family should be taught how to use it if you have a reaction. Wear a medical ID bracelet.
Treating Insect Bites and Stings
Most bites and stings are treated by:
- washing the affected area with soap and water
- placing a cold compress (a flannel or cloth soaked in cold water) over the area to reduce swelling
Try not to scratch the affected area to avoid infection, and if you’re in pain or the area is swollen, take painkillers, such as paracetamol or ibuprofen.
If you have a more serious reaction, your GP may prescribe other medication or refer you to an allergy clinic for immunotherapy (desensitisation).
Read more about Mosquito Bites?