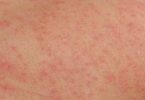
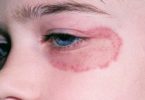
Rosacea is a long-term disease that affects your skin and sometimes your eyes. It causes redness and pimples. Rosacea is most common in women and people with fair skin. It most often affects middle-aged and older adults.
In most cases, rosacea only affects the face. Symptoms can include
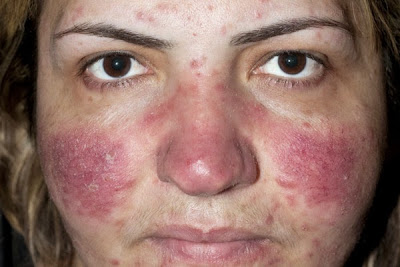
- Frequent redness of the face, or flushing
- Small, red lines under the skin
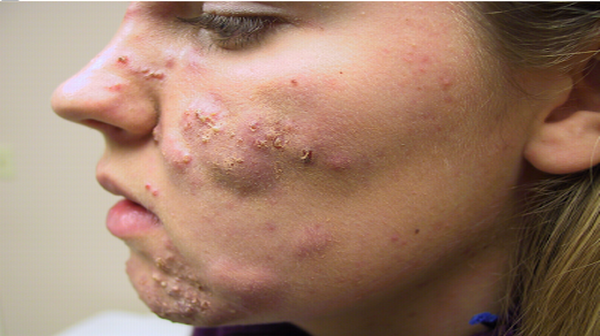
- Acne
- A swollen nose
- Thick skin, usually on the forehead, chin, and cheeks
- Red, dry, itchy eyes and sometimes vision problems
No one knows what causes rosacea. You may be more likely to have it if you blush a lot or if rosacea runs in your family. Rosacea is not dangerous. There is no cure, but treatments can help. They include medicines and sometimes surgery.
The Facts of Rosacea
- Rosacea is a common, chronic, incurable, adult acne-like skin condition.
- Rosacea has periodic ups and downs (flares and remissions).
- Rosacea symptoms tend to come and go.
- Rosacea is easily controllable and medically manageable.
- Rosacea may begin with easy facial blushing or flushing.
- Rosacea commonly affects the central third of the face, especially the nose.
- Rosacea causes tiny red pimples and fine red lines on the facial skin.
- Rosacea may be mistaken for rosy cheeks, sunburn, or quite often, acne.
- Rosacea triggers include alcohol, hot or spicy foods, emotional stress, and heat.
- Rosacea can be a very bothersome and embarrassing condition.
- Untreated rosacea tends to worsen over the time and be a progressive disease.
- Rosacea untreated can cause a bulbous red nose (like W.C. Fields).
- Prompt recognition and proper treatment permit people with rosacea to enjoy life.
What Triggers Rosacea?
The cause of rosacea is unknown, but it could be due to some combination of hereditary and environmental factors.
A number of factors can trigger or aggravate rosacea by increasing blood flow to the surface of your skin. Some of these factors include:
- Hot foods or beverages
- Spicy foods
- Alcohol
- Temperature extremes
- Sunlight
- Stress, anger or embarrassment
- Strenuous exercise
- Hot baths or saunas
- Corticosteroids, such as prednisone
- Drugs that dilate blood vessels, including some blood pressure medications