What's in this article?
What is a fungal nail infection?
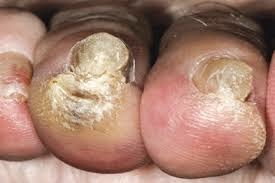
A fungal nail infection occurs when a fungus attacks a fingernail, a toenail, or the skin under the nail, called the nail bed. Fungi (plural of fungus) can attack your nails through small cuts in the skin around your nail or through the opening between your nail and nail bed.
How do you get a fungal nail infection?
- Spread from a fungal skin infection. For example, athlete’s foot is a fungal skin infection of the toes. This may spread to the toenails if the skin infection is not treated early.
- Fingernail infection may occur after a toenail infection has become established. The fungus may spread to a finger if you scratch your itchy toes and toenail.
- Fingernail infections are also more likely to occur if you wash your hands frequently, or have them in water a lot. For example, if you are a cook or a cleaner. Constant washing may damage the protective skin at the base of the nail. This may allow fungi to enter.
- A nail that has recently been damaged is also more likely to become infected.
- You have an increased risk of developing a fungal nail infection if you have various other conditions. For example: diabetes, psoriasis, poor circulation, a poor immune system (for example, if you have AIDS or are on chemotherapy), or a general poor state of health.
- Nail infections are more common in people who live in hot or humid climates.
- Smoking also increases the risk of developing a nail infection.
- In some cases there is no apparent reason. Fungus germs (fungi) are common and an infection can occur ‘out of the blue.
Prevention of fungal nail infection
Good general health and hygiene help prevent fungal infections.
- Do not share tools used for manicures and pedicures.
- Keep your skin clean and dry.
- Take proper care of your nails.
- Wash and dry your hands thoroughly after contact with any fungal infection.
Treating a fungal nail infection
Treatment is not always needed if your infection is mild.
Otherwise, your GP may send a clipping of your nail to a laboratory for tests to find out the exact cause of the infection and to rule out other conditions. They will then discuss appropriate treatments with you.
Fungal nail infections can be treated and usually cured, but some types of treatment can take several months to work. The main treatment options are either antifungal tablets or antifungal nail paint.
Antifungal tablets are the most successful treatment but they may cause side effects. You should discuss this with your GP before deciding which treatment to take.
It is important to ensure you look after your nails properly and practise good foot hygiene to stop the infection returning.
Who gets fungal nail infections?
Between 3 and 8 out of 100 people in the UK will have a fungal nail infection at some stage of their lives. Toenails are more commonly affected than fingernails. It is more common in people aged over 55, and in younger people who share communal showers, such as swimmers or athletes.