What's in this article?
What is Viral infection?
Viral infections occur when viruses enter cells in the body and begin reproducing, often causing illness. Viruses are tiny germs that can reproduce only by invading a living cell. It can also be caused of different kinds of viruses, which the influenza-virus is best known. With a viral infection you usually have a fever, but other complaints can range from abdominal pain and diarrhoea to coughing and shortness of breath.
Types of Viral infections
Probably the most common viral infections are:
Respiratory infections: Infections of the nose, throat, upper airways, and lungs
The most common respiratory infections are upper respiratory infections, which include sore throat, sinusitis, and the common cold.
Other viral respiratory infections include influenza and pneumonia.
In small children, viruses also commonly cause croup (which is inflammation of the upper and lower airways, called laryngotracheobronchitis) or lower airways.
Respiratory infections are more likely to cause severe symptoms in infants, older people, and people with a lung or heart disorder.
Other viruses infect other specific parts of the body:
Gastrointestinal tract: Infections of the gastrointestinal tract, such as gastroenteritis, are commonly caused by viruses, such as noroviruses and rotaviruses.
Liver: These infections result in hepatitis.
Nervous system: Some viruses, such as the rabies virus and the West Nile virus, infect the brain, causing encephalitis. Others infect the layers of tissue that cover the brain and spinal cord (meninges), causing meningitis or polio.
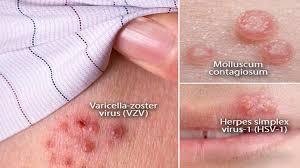
Skin: Viral infections that affect only the skin sometimes result in warts or other blemishes. Many viruses that affect other parts of the body, such as chickenpox, also cause a rash.
Some viruses typically affect many body systems. Such viruses include enteroviruses (such as coxsackieviruses and echoviruses) and cytomegaloviruses.
How Long Do Viral Infections Last?
In most types of viral infection, the immune system clears the virus from the body within days to a few weeks. But some viruses cause persistent or latent * infections, which can last for years. In these cases, a person may get infected and seem to recover or may not be aware of being infected at all. Then years later, the illness will occur again, or symptoms will start for the first time. Viruses that can cause latent infections include herpesviruses, Hepatitis B and C viruses, and HIV.
A viral infection is a common name for several kinds of diseases caused by viruses. What these diseases have in common, aside from viruses, is symptoms like fever and fatigue, which makes you feel miserable.
There are different kinds of viruses; gastro-intestinal-viruses and viruses of the airways are the most important viruses in this case, because they most often cause fever and fatigue. Other viruses cause more local symptoms, like laryngitis, cold sores and shingles.
Antibiotics don’t help when you have a viral infection and a doctor usually shouldn’t prescribe an antibiotic, because only a small percentage of people with general complaints like fever and fatigue have a bacterial infection. Doctors also shouldn’t prescribe antibiotics ‘just to be sure’, because bacteria can get used to the antibiotics and become resistant, so when they’re really needed, threre’s a chance they won’t be effective anymore.
Difference Between Bacteria and Virus
Viruses and bacteria are two types of potentially disease-causing (pathogenic) particles. Viruses are much smaller than bacteria and can’t reproduce without the assistance of a host. Bacteria are capable of reproducing on their own. The symptoms of viral and bacterial illnesses are sometimes similar. A doctor can determine the underlying cause of an illness based on the patient’s symptoms and other factors. Lab tests may help clarify whether an illness is due to a virus, bacteria, or other infectious agent or disease process.
Viruses can be transmitted in a variety of ways. Some viruses can spread through touch, saliva, or even the air. Other viruses can be transmitted through sexual contact or by sharing contaminated needles. Insects including ticks and mosquitoes can act as “vectors,” transmitting a virus from one host to another. Contaminated food and water are other potential sources of viral infection.
How Viral Infections can be Treated?
Viruses cannot be treated with the antibiotics that kill bacteria. Fortunately, a few drugs, such as ribavirin and acyclovir, can control the spread of viral invaders without destroying host cells. Intense research to find better treatments for AIDS has led to development of many drugs that help fight the virus. Unfortunately, none of these drugs has been able to treat viral infections as effectively as antibiotics treat bacterial infections.


Leave a Comment