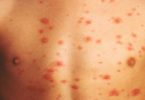
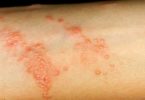
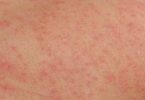
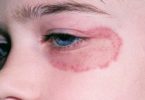
Strep Rash – What is Strep Rash in Kids?
Symptoms of strep throat, which is very common among kids and teens, include fever, stomach pain, and red, swollen tonsils.
Strep throat usually requires treatment with antibiotics. With the proper medical care along with plenty of rest and fluids a child should be back to school and play within a few days.
How Strep Throat Spreads
Anybody can get strep throat, but it’s most common in school-age kids and teens. These infections occur most often during the school year when big groups of kids and teens are in close quarters.
The bacteria that cause strep throat (group A streptococcus) tend to hang out in the nose and throat, so normal activities like sneezing, coughing, or shaking hands can easily spread infection from one person to another. Someone whose strep throat isn’t treated is most likely to spread the infection when the symptoms are most severe, but can still infect others for up to 3 weeks.
That’s why it’s so important to teach kids the importance of hand washing good hygiene can lessen their chances of getting contagious diseases like strep throat.
Strep Throat – Symptoms
Common symptoms of strep throat in children and adults include:
- Severe and sudden sore throat without coughing, sneezing, or other cold symptoms.
Pain or difficulty with swallowing.
Fever over 101°F (38.3°C). Lower fevers may point to a viral infection and not strep.
Swollen lymph nodes in the neck.
White or yellow spots or coating on the throat and tonsils.
Bright red throat or dark red spots on the roof of the mouth at the back near the throat.
Swollen tonsils, although this symptom may also be caused by a viral infection.
In teens, mononucleosis can cause a severe sore throat that looks like and has symptoms similar to those of strep throat. For more information, see the topic Mononucleosis (Mono).
It is easy to tell when you have a sore throat or a cold. It is harder to know when you have strep throat. Typically, sore throats are caused by a viral infection and not strep bacteria. Strep throat usually does not occur with cold symptoms such as coughing, sneezing, or a runny or stuffy nose. The more cold symptoms you have, the less likely it is that your sore throat is a strep infection.
What to Do
If you suspect strep throat, or if your child has been in close contact with another child diagnosed with strep throat, see the doctor right away. Until your child is seen by a doctor, you should keep her away from other children as much as possible. Your pediatrician will take a history and examine your child’s throat. Sometimes the appearance is “obvious strep.” A test, known as a rapid strep test, can be done in the office; the doctor takes a throat swab and tests the sample. This takes approximately five minutes and is around 95 percent accurate in diagnosing strep. However, in some cases the rapid strep test will miss true cases of strep throat in children. A negative rapid strep test should be followed by a throat culture. This involves taking another throat swab and placing the contents of the swab on a special culture that will grow strep bacteria if present. This test takes forty-eight hours to complete and is considered the most accurate. A negative throat culture can almost completely rule out strep as the cause of your child’s symptoms.
Treatment
If strep throat is confirmed, it should be treated with antibiotics, even if your child seems to be feeling better. Sore throats from strep will usually improve on their own; however, treating strep throat in children with antibiotics is still necessary because:
- Your child is still contagious even after her symptoms are improving. If she is treated with antibiotics, she will no longer be contagious twenty-four to forty-eight hours after beginning treatment. Children can be contagious for up to twenty-one days When not treated with antibiotics.
- Symptoms will be alleviated faster with antibiotic treatment.
- Treatment with antibiotics prevents complications of strep throat in children, covered below.
As more and more bugs become resistant to drugs, occasionally strep throat in children does not respond to the usual milder antibiotics. If your child has not improved within two to three days, contact your pediatrician.